Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): A 2025 Survival Guide

- Optimize your content for AI-generated answers by using clear headings, lists, and factually accurate information to increase your chances of being cited by large language models like ChatGPT and Google’s AI Overview.
- Focus on building your topic authority and trust signals through authoritative sources and consistent brand mentions across multiple platforms, as AI engines prioritize known entities.
- Ensure AI models can efficiently crawl your site by using llms.txt files, adding structured data, and reducing reliance on client-side rendering to improve your content's visibility in AI-generated responses.
- Adapt your content strategy to longer, conversational queries as users increasingly search through AI interfaces, and adjust your SEO practices to GEO-focused optimizations for maximum visibility.
- Gain a competitive edge by continuously monitoring and adapting to changes in how AI sources content and ensuring your brand is included in authoritative summaries and cited by trusted entities.
You didn’t lose your rankings. You lost the click.
AI Overviews now show up on more than half of Google searches. ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini are rewriting how people find answers. They skip the page entirely. The best your content can hope for? A citation, if you’re lucky.
We’re all seeing it. Top-funnel pages that once pulled in steady traffic are now getting ghosted. AI Overviews show up in over 55% of Google searches, and they’re answering the question before your page even loads. The user gets what they need, and they’re gone. And that top organic result’s CTR fell from 28% to 19% almost overnight.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is how you adapt. It’s how you stop writing for Google and start structuring for LLMs. GEO is how brands stay relevant in a search environment where the user journey begins and ends inside an LLM response.
This isn’t about traffic anymore but about survival in a search model that doesn’t want to send users anywhere. And it’s happening faster than most teams realize.
In this guide, you’ll learn what GEO really means, how it works, and the tactical steps to get your content cited across Google’s AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Bing Copilot, and Perplexity.
Let’s get into it.
What Is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization, or GEO, is the process of optimizing content to be selected and cited by large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Google’s AI Overviews, Perplexity, and Bing Copilot. Unlike SEO, GEO doesn’t aim to rank pages in blue-link results, it’s about training AI engines to pull your content into their responses.
Generative Engine Optimization Definition
GEO is a strategic response to how users now search. In 2025, tools like ChatGPT and Perplexity pull information directly into their answers, bypassing the need to click. That means if your content isn’t structured for retrieval, it’s invisible.
Think of GEO as optimizing for answers, not pages. It involves using clear formatting (headings, lists, Q&A), maintaining factual precision, and building topic authority so when someone asks a question in an AI interface, your content gets cited.
Wix even built a dedicated “AI Visibility Overview” tool to help users track GEO performance, showing how quickly this strategy is becoming essential.
GEO vs Answer Engine Optimization (AEO)
GEO and AEO both focus on visibility in rich answer formats but they’re not the same. AEO was about showing up in featured snippets on Google’s results page. GEO is about being included within the actual AI-generated response, often without a link or click at all.
Where AEO was a play for position zero, GEO is a play for answer integration.If we are talking about GEO, that means we are talking about learning how LLMs think, what patterns they follow, what sources they trust, and what formats they understand best.
Generative Engine Optimization vs Traditional SEO
Let's clarify something first, geo generative engine optimization (GEO) isn't here to replace traditional SEO. They're complementary approaches, each with specific strengths and roles.
What They Have in Common:
- Quality Matters Most
Just like traditional SEO, GEO values genuinely helpful content. If your page ranks highly in Google, it probably meets user needs clearly and effectively. Generative AI models like ChatGPT and Google’s AI mode value that exact type of content, too, because their goal is similar. (i.e give users the best answer quickly.)
- Authority and Trust Are Essential (E-E-A-T)
Both SEO and GEO reward authoritative sources. For example, HubSpot ranks high on Google’s first page for “CRM” because it’s seen as trustworthy.
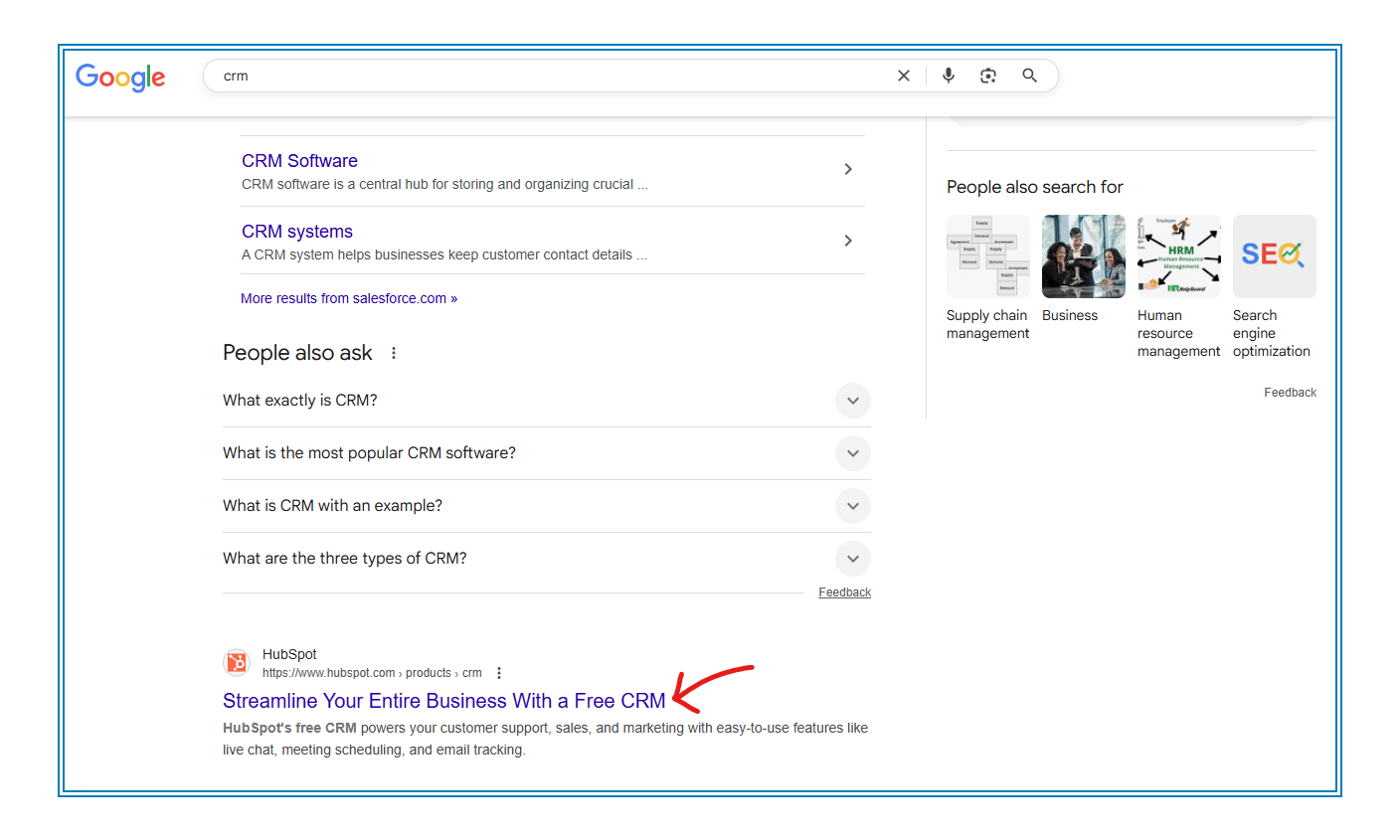
ChatGPT does the same and recommends HubSpot as a reliable CRM tool because it recognizes the brand’s expertise and authority from multiple trusted sources across the web. Simply put, building genuine trust and authority helps you in both areas.
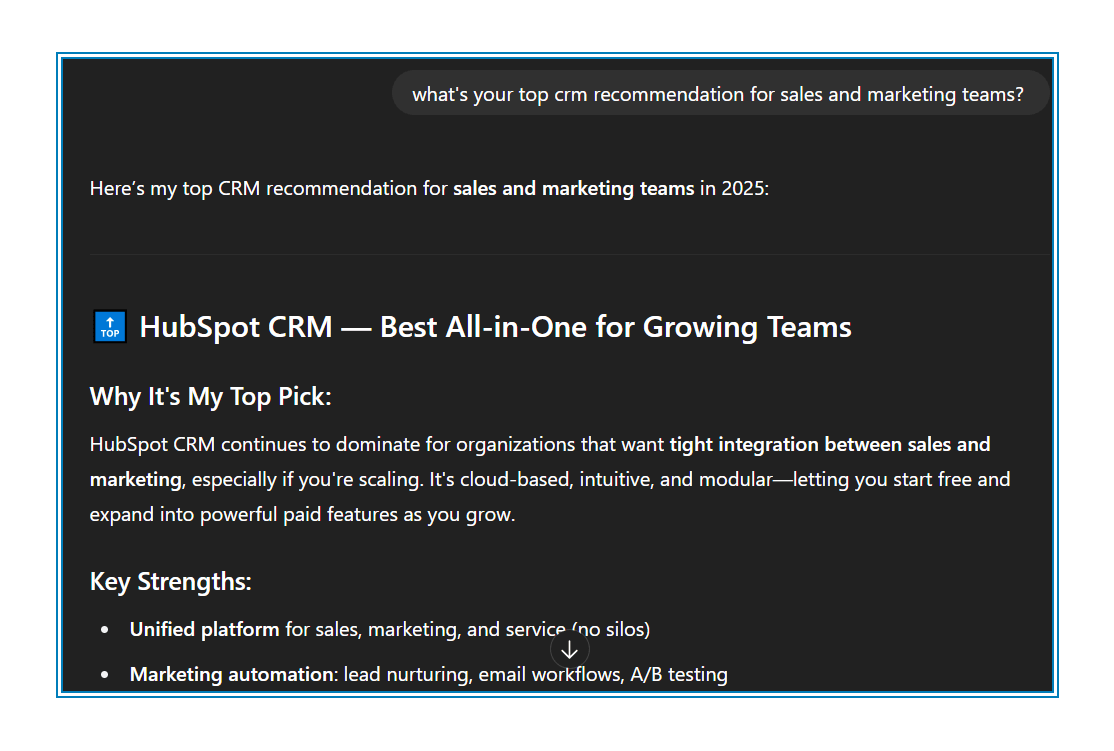
- Keywords Still Guide Users (but differently)
Keywords haven’t vanished, but how users input them has changed. Traditional SEO typically handles shorter keywords like "best CRM software," whereas GEO deals with more conversational, longer queries like, “what CRM software works best for small businesses?” Your keyword strategy still matters. It just needs to be broader and more conversational.
How GEO and SEO Differ
1. Different Goals and Outcomes
Traditional SEO is straightforward: optimize your content to rank high and attract clicks. GEO aims at something different. It’s about optimizing content to be directly included in AI-generated answers. In GEO, you’re trying to get your brand mentioned inside an AI response, even if the user never clicks through. The real value here is brand awareness and authority, rather than click-through traffic alone.
2. Clear Structure Beats Keyword Density
Traditional SEO emphasizes backlinks and keyword density, but the best generative engine optimization strategies for AI involve structuring your content clearly, prioritizing entity clarity, and optimizing for conversational queries.
For example, Chris Long from Go Fish Digital found through testing that generative AI platforms strongly favor structured, list-style content when choosing snippets for their responses. He noted specifically:
- Structured headings (H2, H3)
- Bullet-pointed lists
- Clear summaries
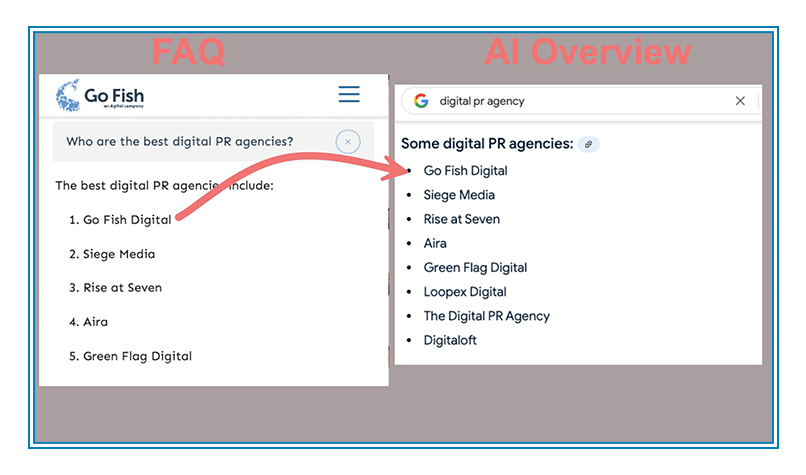
Why Entity Clarity, Trust, and Concise Summaries Beat Keyword Stuffing:
Entity Clarity
Generative AI engines prioritize clear, trusted entities, brands and names they can recognize and confidently recommend. Unlike traditional SEO, where keyword-rich domains could give you an advantage, GEO prefers clearly identifiable brand names.
For example, a domain like "beststlouisSEO.com" might rank well traditionally but likely won't show up in generative AI answers because the AI doesn’t clearly identify it as a trustworthy brand. Instead, it favors known entities like HubSpot, Salesforce, or Monday.com.
Concise Summaries
AI-driven search engines thrive on quick, concise answers that neatly fit user questions. Long, keyword-heavy paragraphs won't perform as well. GEO rewards content that's organized, straightforward, and easy for the AI to integrate directly into its answers.
Trust and Credibility
GEO places immense importance on trust signals from multiple credible third-party sources (like reviews, trusted directories, podcasts, or widely recognized websites). It’s less about backlinks alone, and more about how widely and authentically your brand is discussed online.
AI models scan content from many sources, picking brands consistently mentioned positively by trusted entities. This is different from traditional SEO, which primarily values backlink authority.
How Does Generative AI Work?
Generative AI models don’t just retrieve answers but build them from scratch using what they’ve learned from huge amounts of data.
Let’s walk through what’s happening under the hood.
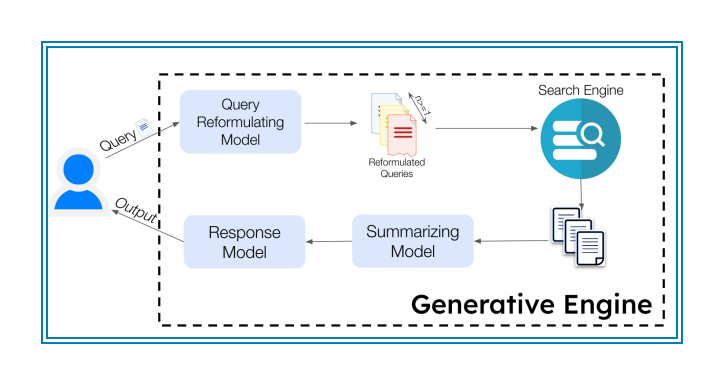
Step 1: Query Reformulation
When you type in a question, the engine doesn’t run with it as-is. A Query Reformulating Model rewrites the question in a way that makes it easier to find relevant sources. This helps the system understand what you're really asking, especially if the original query is vague or complex.
Step 2: Document Retrieval
That reformulated query gets sent to a search engine, which fetches documents that might contain helpful information. This could be web pages, research papers, or trusted third-party sources.
Step 3: Summarization
Once those documents are collected, a Summarizing Model extracts the key points. This part matters most for GEO – content that’s clearly structured, accurate, and easy to digest stands a better chance of being selected here.
Step 4: Response Generation
A Response Model takes the summaries and generates the final answer. The response is assembled by analyzing the patterns across the retrieved content. This is where your brand, if cited correctly, could show up directly in the answer itself.
What Is Generative AI vs Traditional AI?
Let’s keep this simple:
- Traditional AI (what some call “predictive AI”) is built for structured tasks. It looks at labeled data, follows fixed rules, and gives back defined outputs like a number or a category. Think: fraud detection or sales forecasting.
- Generative AI is trained on a much wider range of inputs, including unstructured data like text, images, and audio. It can generate new content that didn’t exist before. Instead of labeling content, it creates it.
As Brad and Satish noted in their discussion, traditional AI is optimized for tasks with clear boundaries and rules. Generative AI can handle open-ended prompts, work with messy inputs, and generate more flexible, creative responses.
So while traditional AI is more like a calculator, generative AI acts more like a collaborator.
What’s the Best Generative Engine Optimization Strategy for AI Products?
If you're building or marketing an AI product in 2025, you can't afford to ignore Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). As we discussed earlier, GEO doesn't replace SEO, instead it builds on it. But the way you structure, position, and distribute content changes once your goal becomes earning a spot in AI-generated answers.
Here’s how to make sure your product gets surfaced by generative engines like ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, or Google’s AI Overview.
Generative Engine Optimization Best Practices 2025
1. Use Traditional SEO as Your Baseline
AI models often start with Google’s top-ranked content. If your page ranks well for a relevant term, you already have a head start. GEO just layers on a few extra requirements to get from “visible” to “quoted.”
2. Get Featured in Authoritative Content
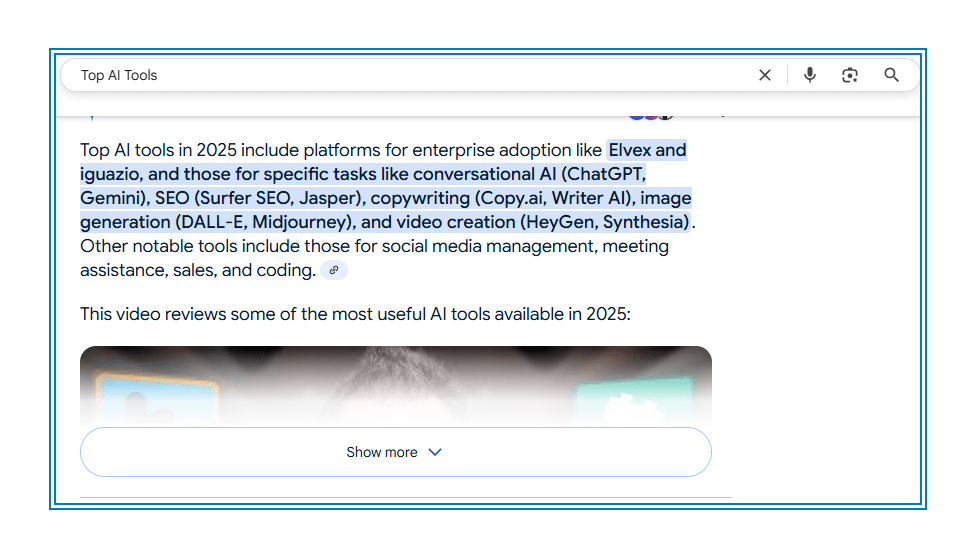
Generative models love trusted summaries. That’s why listicles, directories, and comparison posts are so often quoted. Make sure your AI product appears in “Top AI Tools,” “Best CRM for Data Teams,” or similar lists especially if they’re already ranking on page one or indexed by Wikipedia.
3. Structure for AI Skim-Reading
Clarity beats cleverness. Use H2 and H3 headings in question-answer format. Keep paragraphs short. Add bullet lists where possible. AI models don’t skim like humans, but they do favor content that’s well-structured and easy to summarize. The more declarative your statements, the better. Think:
“Over 92% of enterprise users rated our platform as easy to deploy.”
Instead of:
“Customers are generally happy with the onboarding experience.”
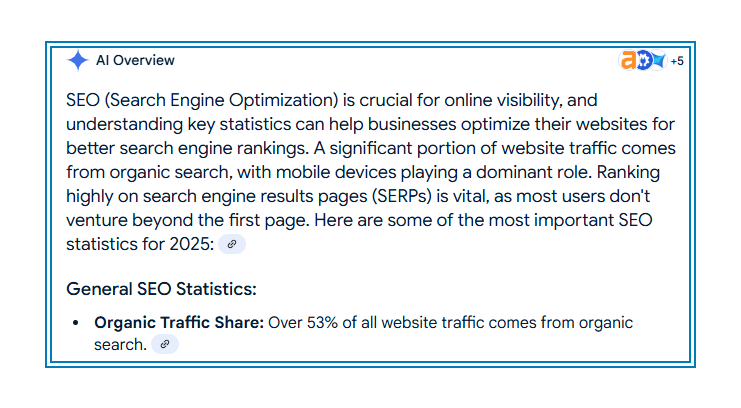
4. Implement Schema and llms.txt
Structured data still matters. Use schema types like FAQPage, Product, and HowTo to give your content semantic clarity. And don’t forget to add an llms.txt file. As noted earlier, this is your way of guiding LLMs to your best, AI-friendly pages. Think of it like an index specifically for generative crawlers.
→ This is how LLMs Use llms.txt to discover content
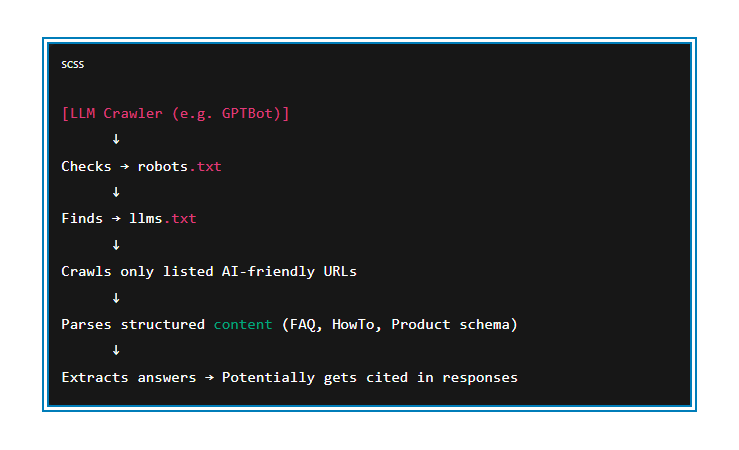
5. Make Sure AI Can Crawl Your Sit
LLMs can’t parse JavaScript-heavy pages or gated content. Open up access in your robots.txt, reduce reliance on client-side rendering, and deliver clean HTML. If your content can’t be rendered, it won’t be read. And if it can’t be read, it definitely won’t be cited.
(Failed Crawl)

(Successful Crawl)
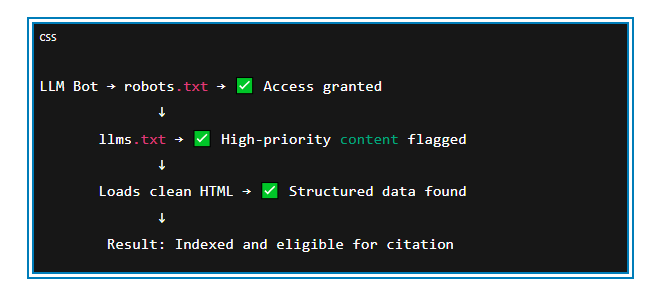
6. Build Authority and Consistency Across the Web
Generative models tend to cite brands that are talked about consistently across multiple platforms. Ensure your messaging is aligned across your website, GitHub repos, LinkedIn, and external publications. A fragmented footprint makes you harder to trust, both for users and AI engines. This kind of brand consistency often falls under the umbrella of AI marketing services, especially when it includes tools like AI-driven brand monitoring, prompt training, and cross-platform content alignment.
7. Tap Into User-Generated Discussions
Sites like Reddit, Stack Overflow, and Quora feed directly into the LLMs’ training data. So do product review sites like G2 and Capterra. Instead of relying solely on your owned content, look at where your users talk. Then, make sure you’re part of that conversation.
8. Earn Third-Party Mentions That AIs Trust
Unlike traditional SEO, you can’t always rely on backlinks to do the heavy lifting. AI engines care more about third-party credibility. That means getting featured in relevant blogs, research reports, media mentions, or cited in expert roundups.
9. Stay Alert and Adaptive
AI sourcing behavior changes fast. If you’re seeing more citations coming from GitHub repos, YouTube transcripts, or Reddit threads, shift your strategy accordingly. GEO is a moving target, and brands that monitor and adapt will win the early advantage.
Generative Engine Optimization Checklist for AI Products
- Make your site crawlable by LLMs (robots.txt, llms.txt)
- Add structured data (FAQ, HowTo, Product)
- Get your product listed in high-authority listicles and directories
- Maintain consistent brand descriptions across all platforms
- Stay active in relevant forums and review platforms
- Track AI mentions and citations (ChatGPT, Claude, SGE, etc.)
- Focus on truth, clarity, and helpfulness in every piece of content
Teach Your Team to Actually Use AI
We train your marketers to confidently use AI across strategy, content, and execution inside the tools they already rely on.
How to Do Generative Engine Optimization (Step by Step)
Doing Generative Engine Optimization isn’t complicated. It follows steps similar to regular SEO but adjusted specifically for AI tools. Here’s exactly what you need to do:
1. Mine buyer questions & intents (prompt/query research)
First, figure out exactly what your potential customers ask AI tools when researching your product or niche. This helps you match your content to the real questions they're using in natural conversations.
- Check your customer support records and sales calls. Find the exact wording your customers use. If your support team hears questions like "Can your tool integrate with Salesforce?" write those down.
- Look into forums and social media conversations. People use Reddit, Quora, LinkedIn, or specialized forums to ask detailed questions about products. Take note of exactly how they phrase these questions.
- Use Google's 'People Also Ask' and related search suggestions. These sections provide common questions your audience is already asking online.
- Example: Instead of just targeting "best CRM," aim for specific queries like "What's the easiest CRM for small SaaS businesses?" or "How does [Your Product] stack up against [Competitor]?"
2. Write answer-ready blocks (Q&A, lists, tight headings)
Next, format your content clearly so AI can easily pull answers. AI tools look for short, clear chunks of information that directly address questions.
- Use clear, question-based headings. For example, if customers often ask "How do I choose the right ERP system?" make that exact question your section heading.
- Answer directly and simply. Provide straightforward answers in just a sentence or two. Don’t add fluff or background info upfront.
- Use lists, bullet points, and numbered steps. AI tools prefer extracting info from structured lists or step-by-step explanations. If the question is "What are the advantages of AI chatbots?" give a quick bulleted list of clear benefits.
- Include specific facts or data points. Instead of vague statements, like we discussed earlier, say something concrete like "92% of users found our platform easy to set up." This kind of straightforward fact is ideal for AI to pick up and share.
3. Add schema (FAQ/HowTo/Product) + implement llms.txt & clean HTML
Now, make sure your content is technically easy for AI to read and understand clearly. As we stated before:
- Use structured data (schema). Add schema like FAQPage, HowTo, or Product. This tells AI exactly what your content is about, improving the odds they'll cite you.
- Create an llms.txt file. This is basically a simple guide for AI crawlers that clearly lists your most important content pages. You put it at your site’s root (like yourdomain.com/llms.txt). It helps AI quickly understand what pages you think are important.
- Simplify your HTML and avoid heavy JavaScript. AI tools can't reliably read content hidden behind scripts or interactive elements. Stick to clean HTML and avoid complex web technologies on important content pages.
4. Track AI referrals/citations, update KPIs
Once you’ve set up your content for GEO, you need to measure if it’s working. Traditional SEO metrics won’t fully capture this, so adjust your KPIs accordingly:
- Regularly test with AI tools manually. Ask ChatGPT, Bard, Bing Chat, or Perplexity the questions you targeted. See if they mention your product or site.
- Use AI tracking tools. Semrush or other platforms offer AI citation tracking. They show how often your brand or product is mentioned compared to competitors.
In Semrush AI Toolkit, you'll find clear metrics:
↪ Market Share: This tells you how often your brand comes up in AI responses, compared to the total mentions collected. Basically, it shows how much AI engines talk about you overall.
↪ Brand Performance Report: Here, you can see how your brand is doing on different AI platforms side-by-side. It helps you quickly figure out where you’re ahead or behind your competitors.
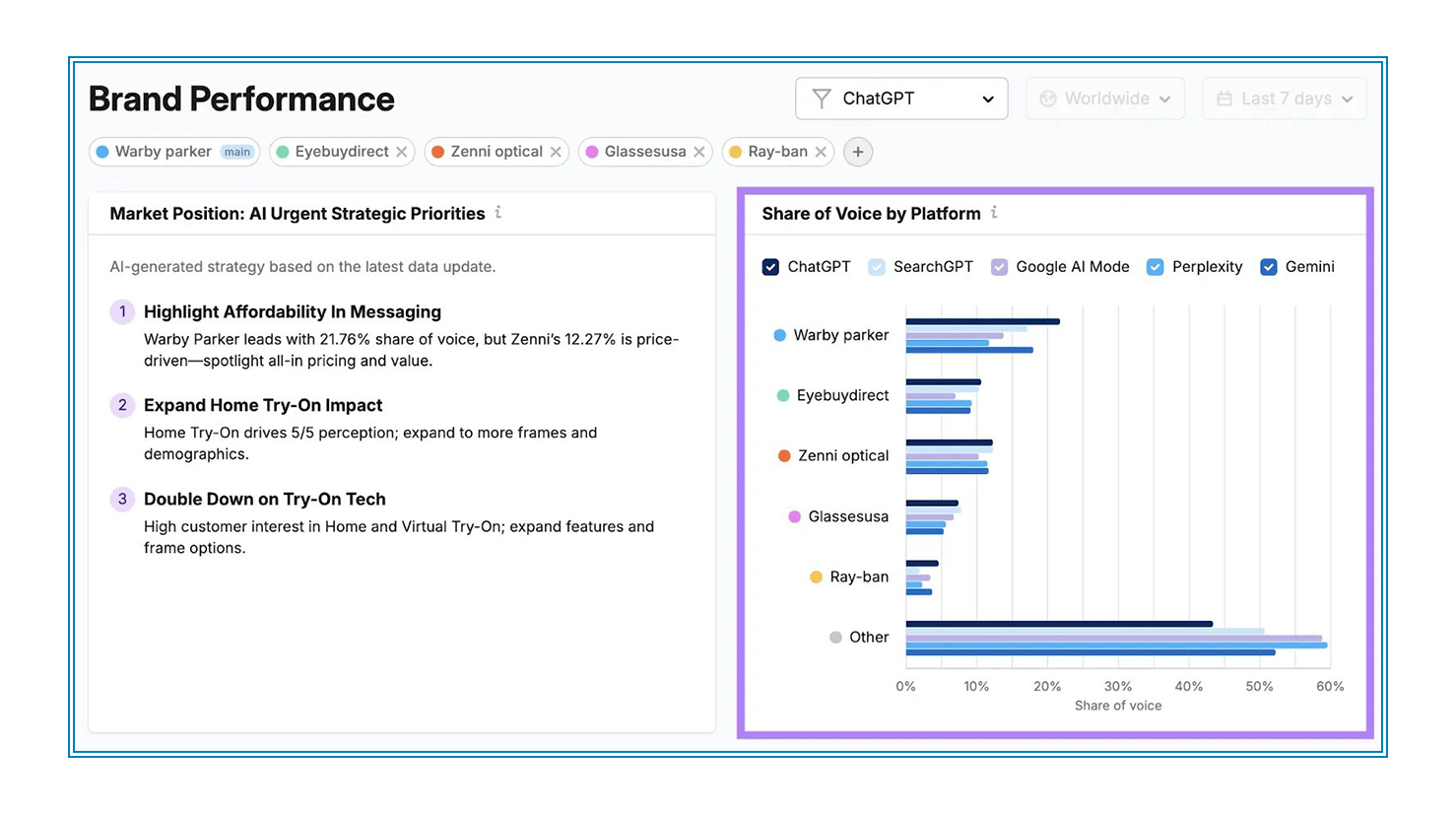
↪ Share of Voice by Platform: This shows your brand’s presence on each individual AI tool. For example, you can clearly spot if you’re mentioned more often on ChatGPT compared to Gemini or Perplexity, so you know where to focus more attention.
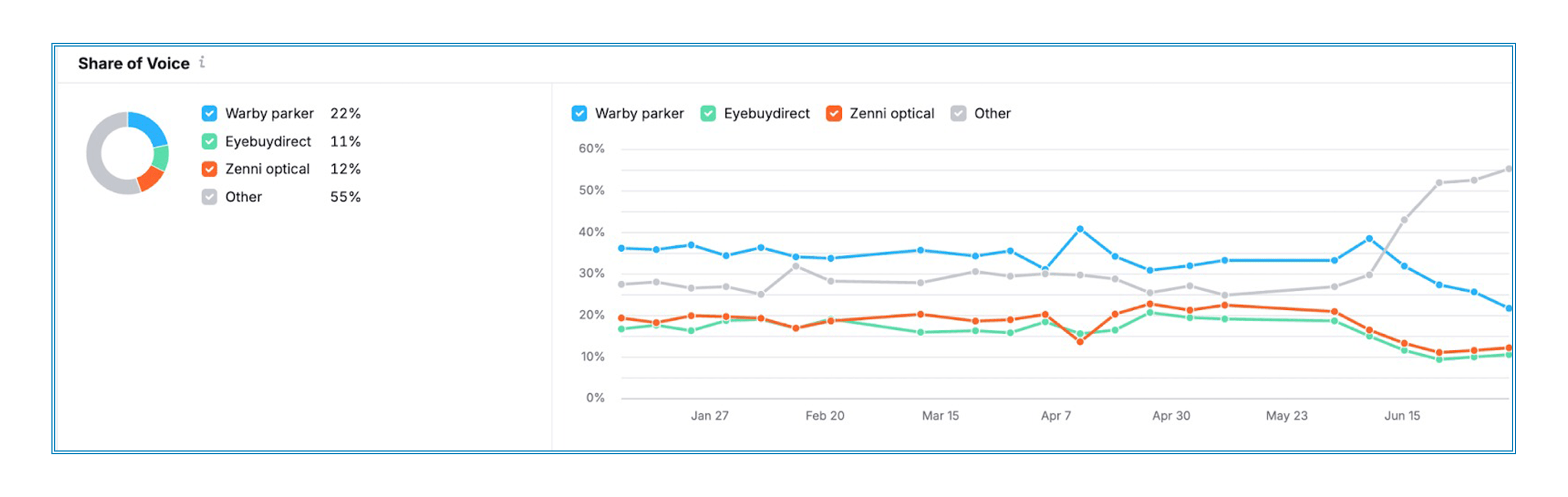
- Adjust your KPIs. Start tracking metrics like AI citation count, traffic from generative tools, and sentiment of mentions. This gives you clear numbers on how well your GEO is doing.
5. Refresh content for re-ingestion
Finally, your content can’t just sit still. AI engines periodically update their knowledge bases. Keep your content fresh and accurate to stay relevant in these updates:
- Regularly audit and update your content. Every few months, review your key pages. Add new answers to emerging questions your audience asks.
- Update facts, numbers, or examples. If your product changes or you have updated data, refresh your site immediately. AI prefers up-to-date content.
- Signal clearly when you've updated. Use timestamps (like <lastmod> in your sitemap) or notes showing updates. This signals to AI your content is current.
This is how to use <lastmod> to signal ai and search engines your content is fresh
Step 1: Locate or Generate Your Sitemap
- If you're using WordPress with Yoast or RankMath, your sitemap is usually auto-generated.
- Example URL: yourdomain.com/sitemap_index.xml or yourdomain.com/post-sitemap.xml
- Example URL: yourdomain.com/sitemap_index.xml or yourdomain.com/post-sitemap.xml
- If you don’t have one, generate it using XML-Sitemaps.com or an SEO plugin.
Step 2: Add or Edit the <lastmod> Tag for Each URL
A sitemap entry should look like this:
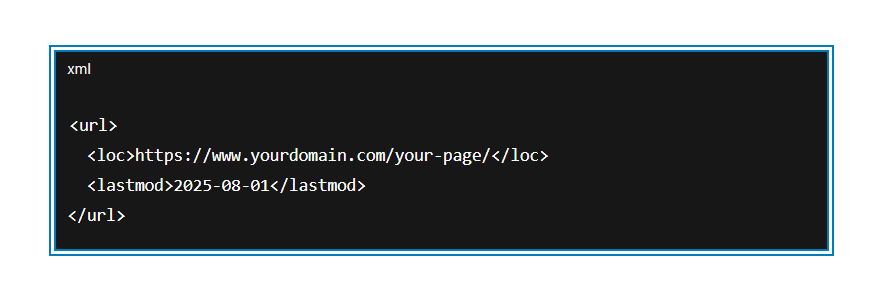
- The <lastmod> tag tells crawlers the last time the page was updated.
- Format is: YYYY-MM-DD
Step 3: Update <lastmod> Every Time You Update the Page
- Manually change the date when you publish updates.
- If using a CMS like WordPress, some SEO plugins (like Yoast or SEOPress Pro) can do this automatically when the page is saved.
Step 4: Resubmit the Sitemap in Google Search Console
- Go to Google Search Console
- Navigate to: Index > Sitemaps
- Paste in your sitemap URL and click Submit
- This helps AI engines (like Google’s AI Overview) and traditional crawlers know to re-crawl the page.
Real Examples To Evaluate Differences In LLMS
To show how LLMs weigh the same question differently, we asked four engines “What is the best project-management software for small teams?” and compared the results.
- Google AI Overviews
Google echoed its page-one results: Asana, Trello, ClickUp, monday.com, Wrike. It leans hard on strong organic rankings, so if you are not already winning classic SEO, GEO visibility here is tough.

- Bing Copilot
Copilot led with monday.com, calling it “highly flexible,” then listed Asana and ClickUp. Copilot pulls live Bing SERPs but also rewards Product schema and clean HTML. If your page is quick to parse and well-marked-up, Copilot will see you even without top-three rankings.

- ChatGPT (GPT-4)
ChatGPT’s list started with Trello, Asana, ClickUp. Because GPT-4 relies on a late-2024 snapshot sometimes, it mirrors evergreen listicles. If those roundup posts haven’t mentioned you, GPT-4 won’t either, no matter how fresh your new blog post is.

- Perplexity
Perplexity surprised us by elevating Plaky and Smartsheet alongside Trello and Asana. It scans newer blog articles, Reddit threads, and even pricing PDFs. Brands active in discussion forums or new “Top X” posts can jump ahead quickly here.
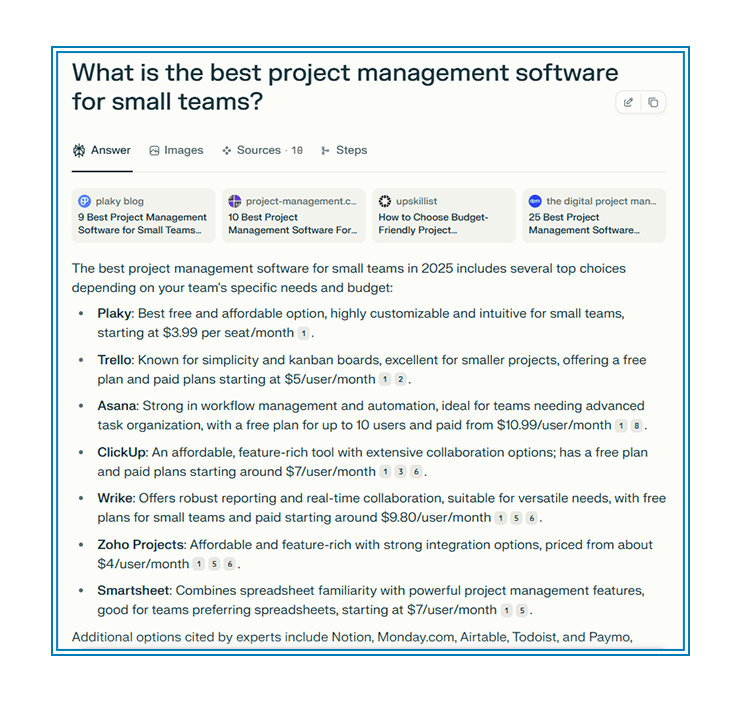
Each engine favors a different mix of authority (Google), structure (Copilot), historical listicles (ChatGPT), or fresh community chatter (Perplexity). A solid Generative Engine Optimization plan means covering all four bases: keep ranking pages sharp, add schema and an llms.txt, secure mentions in authoritative listicles, and stay present in lively community threads.
Measure Success: New GEO KPIs
Modern GEO isn’t judged by blue-link rankings alone. Once your content is “AI-visible,” these three metrics tell you whether that visibility is paying off.
1. AI Citation Share
Think of this as SERP market-share for generative search. It’s the percentage of all prompts in a tracked dataset where an LLM (ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, etc.) cites your brand. A practical way to collect it is with a third-party monitor such as the Semrush AI Toolkit, which automatically runs thousands of relevant prompts and logs every brand mention.
2. AI Referral Traffic
Citations are nice, clicks still pay the bills. Add a “Generative AI” channel group in Google Analytics (or similar) so visits that arrive from chatbots (often via unique referrers or UTM tags) are separated from organic search. Watch not only volume but conversion rate, early studies show chatbot traffic often converts at a higher clip because the user arrives mid-funnel.
3. Answer-Block Coverage
For each priority query, ask: “Are we the source for at least one paragraph, list item, or table in the AI answer?” Track yes/no in a simple sheet, then note which competitors own the blocks you don’t. Over time, aim for growing coverage rather than fixating on one exact prompt, because wording shifts constantly.
Quick sanity check
- Benchmark first. Run a baseline crawl so leadership can see where you stand today.
- Update quarterly. LLM training snapshots lag, give updates time to surface.
- Correlate with revenue. Cite-share looks great on a slide, but tie gains to pipeline or sales before declaring victory.
FAQs
Is ChatGPT generative AI?
Yes. ChatGPT is a generative large-language model (LLM) that uses patterns in its training data to create new text on demand. So it’s both an LLM and a form of generative artificial intelligence.
Is ChatGPT an LLM or generative AI?
It’s actually both. “LLM” describes the underlying model size and architecture, while “generative AI” describes what the model does, such as generate original-sounding text, code, or answers from learned patterns.
What is agentic AI vs generative AI?
Generative AI produces new content when you ask for it. Agentic AI goes a step further: it can plan and execute multi-step tasks (think “book a flight, then email the receipt”) by chaining smaller AI actions together. In short, generative creates; agentic acts.
What is generative artificial intelligence, and how does it work?
Generative AI learns from huge data sets, spots patterns, and then samples from those patterns to produce fresh content (text, images, even code) that wasn’t in the original data. Techniques like transformer neural networks and unsupervised learning let the model predict the most likely next word, pixel, or note.
Why does generative engine optimization (GEO) matter now?
LLMs such as ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, and Perplexity increasingly answer user queries directly. GEO ensures your content is structured, trusted, and easy for those engines to cite putting your brand inside the answer instead of waiting for a click.
In The End
Large-language models are now the first (and often only) stop for many searchers, so classic blue-link rankings deliver a fraction of the clicks they used to. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) addresses that shift by structuring your content for LLMs. Authority still matters but entity clarity, concise summaries, and third-party credibility now outweigh raw keyword density.
Mine the conversational queries your market feeds to ChatGPT or Google’s AI Overviews, write answer-ready sections, add schema plus llms.txt, monitor AI citations/traffic as new KPIs, and refresh pages so they’re re-ingested in future training snapshots.
Done right, your brand shifts from hoping for a click to becoming the quoted source inside the answer.
GEO Is Changing Fast.
Don’t Fall Behind. Speak with a strategist who can assess your current visibility and build a plan.